At our clinic in Düsseldorf, ear pinning is one of the procedures that requires relatively little effort but has a very positive effect on the aesthetics of the face.
Protruding ears can be given a very good aesthetic shape by creating them. We can also treat very large ears or various ear deformities with an ear correction.
Our team of plastic surgeons distinguishes between various options for the procedure:
- The classic surgery for ear reshaping is called auricle reshaping surgery (OMAP for short) and is the most commonly used form of ear correction.
- Minimally invasive ear placement (also known as the suture method ) is the most commonly used method for ear placement in our clinic.
- Ear reduction is performed much less frequently with similar surgical effort. Ear reduction can be combined with ear pinning.
- We perform an earlobe correction to reduce the size of the earlobes.
- Ear reconstruction sometimes involves very complex techniques using donor cartilage.
- Incidentally, it is possible to place the baby’s ears shortly after birth without surgery.
Contents
Yuveo Clinic
Special features of ear correction
At the Yuveo Clinic, we can shape protruding ears aesthetically with gentle procedures that leave few scars.
Ear pinning surgery at our clinic in Düsseldorf
We can perform ear correction on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia, possibly with additional sedation. General anesthesia is common for ear correction in children, anxious adolescents and adults.
The hair and ears must be washed thoroughly before the procedure. After the operation, we only apply a larger bandage for 2 to 3 days.
Before the ears are fitted, we decide together with you to what extent this is necessary:
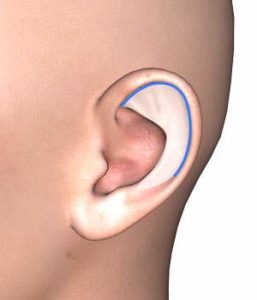
- Ear correction in the sense of ear pinning by forming the missing middle auricle fold (anthelix fold).
- Rotation of the auricle to make it appear smaller.
The following measures may also be appropriate:
- Ear reduction or auricle reduction
- Earlobe correction
Frequently asked questions about creating protruding ears
Here we present an option for ear placement:
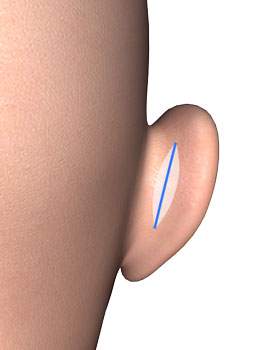
We make an approx. 4 cm long incision in the auricle behind the ear and expose the cartilage.
We then have to weaken the ear cartilage on the front side at the point where the fold is to be formed using a fine rasp. This is important for a stable result when creating the ears. This can be done via the incision described above or via a further 3 to 4 mm incision on the front of the ear.
We can now place the cartilage sutures in the desired position.
Most plastic surgeons use transparent, non-self-dissolving sutures to maintain the position in the long term.
Above all, we want to prevent suture reactions with redness, swelling and pain in the ear cartilage, which can occur as a result of the body breaking down the suture.

Special features of the method
- The swelling phase is shorter than with classic ear correction.
- As a rule, there is considerably less pain.
- Removing stitches is less painful or not necessary at all with the suture method, as the incisions are only treated with a single button suture or remain covered with a plaster.
- Depending on the suture technique used, there are no scars or only practically invisible mini-scars.
- For many patients who generally shy away from surgery or anesthesia in the sense of twilight sleep or even anesthesia, our Düsseldorf team has noticed a better acceptance of the suture technique, which can be performed under local anesthesia.
- Nevertheless, the complication rate is comparable to the open technique.
Unfortunately, only a few parents and midwives are aware that protruding ears can be created without surgery!
However, this only works shortly after birth, as the ear cartilage is still soft and easy to shape in the first few days. In this phase, anyone can put on the baby’s ears without surgical training.
Recipe: Take an adhesive plaster and compresses or other soft material and fix the ears in the desired position. This form of splinting should be maintained for 4 to 6 weeks.
The reason for the good deformability of the ear cartilage is attributed to the maternal estrogen (female sex hormone) still present in the infant’s body.
Association
After an ear correction, the ears are molded with absorbent cotton, for example, and enclosed under an initially quite large ear bandage. This remains in place for 1 to 7 days. It reduces swelling and the risk of bruising.
Threads
We remove the stitches behind the ear after approx. 2 weeks, in front of the ear after one week at a check-up appointment at the Yuveo Clinic in Düsseldorf.
Headband
A headband should be worn 24 hours a day for 2 weeks following ear correction. After that, wearing it at night is sufficient for a further 3 to 4 weeks. A little more rigor is required for children. Wearing a cap is an advantage here, at least for smaller children, because it does not slip so easily.
Sport
In order not to jeopardize the result of the ear correction, we recommend that you avoid sports that may cause bruising of the ear for 6 to 12 weeks. This includes team sports and ball sports.
Inner threads
Even if the healing after the ear correction is inconspicuous, the inner stitches can sometimes show through the skin. The skin may also be punctured. If these stitches cause discomfort, we can remove them without any problems.
If they are removed too soon after ear correction, a relapse of the protruding ears can be expected.
Whether the health insurance company will cover the costs of ear pinning depends mostly on the child’s age. There are no major problems in this regard until the child starts school.
After that, however, reimbursement becomes increasingly difficult. Does a child who has survived the first few years of school “unscathed” no longer need such an operation?
In adulthood, the assumption of costs is fairly hopeless. However, the doctors at the medical service of the health insurance companies decide on the medical value of protruding ears (unfortunately not always to the patient’s advantage).

Until the child starts school, the costs of ear pinning for protruding ears are covered by health insurance. The same applies to other ear malformations with a pathological value.
Once the child has started school, it is very difficult to get the statutory health insurance companies to cover the costs.
The costs for ear pinning are made up of various components. The surgery is usually offered under local anesthesia with twilight sleep . The latter is more comfortable for the patient and for the plastic surgeon, but is not absolutely necessary.
General anesthesia is recommended for children and anxious adults. An inpatient stay is rarely necessary after ear pinning.
For more detailed questions about costs, please contact our team of plastic surgeons at the Yuveo Clinic. It is important that you have cost transparency to avoid surprises.
Fact check
- Practitioners: Dr. Schumann and Dr. Schumann-Averkiou
Anesthesia:
local anesthesia with twilight sleep, general anesthesia if necessary- Hospitalization:
outpatient - Aftercare:
1 to 7 days Bandage, cool, elevate upper body, wear headband - Sport:
No sport for 6 to 12 weeks after surgery - Costs: on request
Further information and related topics
- Protruding ears belong to the malformations of the ear
- Detailed information on the creation of protruding ears
- Thread techniques for ear placement
- Other methods that are available to us for ear placement
- What complications can occur during ear placement?
- What role does the size of the pinna play in ear pinning at the Yuveo Clinic in Düsseldorf?
Technical terms
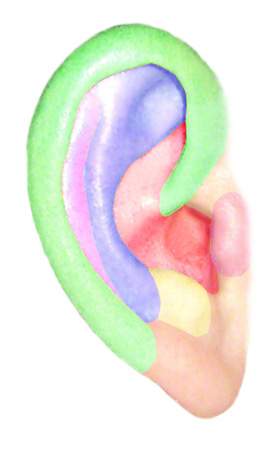
- Anthelix = middle ear fold
- Apostasis otum or otapostasis = protruding ears
- Concha = base of the auricle
- Helix = edge of the auricle
- Macrotia = ears that are too large
- Otoplasty = OMAP = otopexy, otoplasty, anthelixplasty = the surgical correction of protruding ears
- Scapha = curved depression in the auricle
- Tragus (“billy goat”) = the part of the cartilage overlapping the entrance to the auditory canal, usually hairy