Compared to breast augmentation, breast reduction, tummy tuck, etc., calf reduction plays a rather minor role in plastic surgery.
Nevertheless, there are many people (mostly women) who feel at least as much suffering because of their large calves as women who undergo breast augmentation because their breasts are too small, or as women who have their breasts reduced because they are too large.
This article is intended to inform you about the options available. Ultimately, it is a question of subjective suffering whether and for which procedure you decide.
Contents
Yuveo Clinic
Special features of calf reduction
Our plastic surgeons at the Yuveo Clinic Düsseldorf decide which surgical procedure to use to reduce the size of the calves depending on the cause.
Calf reduction through denervation
Too much fat
Too much muscle
Sportsman's vest
Calf reduction through muscle surgery
If the calf muscles are too strong(calf hypertrophy) and are the cause of the increase in circumference, the only way to achieve a significant reduction in calf size is to remove part of the calf muscles.
Patients who decide to undergo this operation usually suffer from severe psychological stress. Men do not wear shorts, women do not wear shorter skirts – swimming pools and beaches are generally avoided. Sometimes it is almost impossible to find boots or ski boots that fit.
Muscle removal
This is the most effective method of calf reduction. The procedure can be performed under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia.
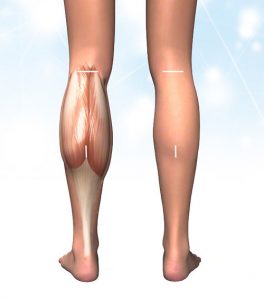
If the skin is of good quality, a 5 cm long transverse incision in the popliteal fossa and a further approx. 5 cm long longitudinal incision in the middle of the lower leg are sufficient (see image). The gastrocnemius muscle can be easily operated on via these approaches. Large nerve and vascular structures of the popliteal fossa are located deeper and are not affected.
After inserting a drain (not always necessary), the wound is closed in several layers.
Effect: Depending on the preoperative findings, the calf circumference can be reduced by around 5-7 cm using this form of calf reduction.
Advantages:
- Maximum effect of calf reduction because the hypertrophied muscle tissue is removed.
Disadvantages:
- More scars
- Greater loss of strength in the short term
- Healthy muscle tissue is removed.
- Especially in calves with very little fatty tissue, the inner contour in the upper calf section looks somewhat unnatural.
Partial removal
However, partial removal of the muscles described is also possible. For example, only the inner muscle belly of the gastrocnemius muscle can be removed.
Frequently asked questions about calf reduction
Why is calf reduction by partial muscle removal possible without functional restrictions?
The actual calf muscle that attaches to the Achilles tendon is the triceps surae muscle(three-headed calf muscle). This in turn consists of the soleus muscle and the two-headed gastrocnemius muscle. The former is essential for function. The latter is an auxiliary muscle, the loss of which does not lead to any change in function.
The function is taken over by other muscles.
For this reason, the gastrocnemius muscle is often used in plastic surgery as a muscle flap for defects in the knee area.
What is an endoscopic partial removal of the muscle?
In Asia, particularly in Korea, endoscopic calf reduction has become established. Here, the gastrocnemius muscle can be reduced via an incision or two incisions of approx. 2 cm in the hollow of the knee. This means that only one part is removed.
The muscle is thinned using an electrocautery (a knife that cuts with electricity and heat). In this way, the natural shape of the calf can be largely preserved.
Advantages:
- Small skin incisions
- Individual shaping of the calves possible
- Short-term loss of strength is minimal.
Disadvantages:
- Healthy muscle tissue is removed.
- Less reduction in calf circumference than with complete muscle removal.
- If it is not possible to shape the cutting surface on the muscle smoothly, contour irregularities may remain visible.
Follow-up treatment:
Intensive stretching exercises must be performed several times a day for several months to prevent excessive scar shrinkage.
Sources:
- Calf reduction by subtotal resection of the gastrocnemius muscle in Asians with calf hypertrophy:
Subtotal resection of gastrocnemius muscles for hypertrophic muscular calves in Asians. – Lee JT, Wang CH, Cheng LF, Lin CM, Huang CC, Chien SH. – Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006 Nov;118(6):1472-83. - Leg re-contouring by using a new technique of partially removing gastrocnemius – Qin RS, Wang X, Chen YZ, Xie HB, Zhu L, Li B, Ma YG, You WT, Li D, Li JN. – Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2003 Mar;19(2):85-7. Chinese.
Can a calf correction be achieved with liposuction?
Calf reduction by liposuction is a good treatment option if the increase in circumference is caused by an accumulation of fatty tissue.
The amount of excess fatty tissue can also be tested by any non-medical professional by squeezing the tissue with two fingers. If there is almost only skin here, the calf consists mainly of muscle. A calf reduction with liposuction is then not promising.
Calf correction by liposuction rarely results in unevenness. The ankles are treated with caution, as swelling and pigmentation changes can occur with radical procedures.
The recovery phase depends on the amount of suction. It can last a few days, but also a few weeks (in the case of extreme findings). In principle, you should refrain from sport for 6 weeks and wear support stockings for the same length of time.
Advantages:
- Calf reduction using liposuction leaves only a few small, barely visible scars (puncture marks).
Disadvantages:
- Only a slight reduction in circumference is to be expected with a high muscle percentage and a low fat percentage in the calves.
Can you achieve a calf reduction with Btx?
One option for calf reduction is using Btx (Bttx A). Btx is a neurotoxin that causes muscle paralysis. Today it is used as standard in the treatment of mimic wrinkles.
The Btx is injected into the muscle without anesthesia via many small punctures (10-15 per side).
The advantages are obvious:
- Calf reduction with Btx is hardly invasive and there are no scars.
- The treatment is easy to perform and requires no surgical skill.
- A recovery phase does not need to be taken into account.
- If you are not satisfied, the calf muscles will be as they were before the treatment after a few months.
Disadvantages:
- Only slight reduction in calf circumference even after multiple applications.
- The result only lasts for approx. 3 – 6 months.
- In the long term, this is a costly method. It must be used at least once every 3 – 6 months and the dose required is high due to the size of the muscles.
Calf reduction with Btx is certainly feasible. However, it is only practiced in rare cases due to the high costs and the relatively small effect. As a patient, you should think carefully about whether the investment is worthwhile.
Source:
Botulinum toxin a for aesthetic contouring of enlarged medial gastrocnemius muscle. – Lee HJ, Lee DW, Park YH, Cha MK, Kim HS, Ha SJ. – Dermatol Surg. 2004 Jun;30(6):867-71; discussion 871.
Can the calf be reduced in size by not exercising?
Calf reduction can be achieved by abstaining from sport. This depends on the extent of the calf muscles.
If the calves are perceived as being too large as a result of heavy exercise, they can be reduced by avoiding certain exercises and forms of training.
Since standing on tiptoe with and without weights, climbing stairs, hiking and sprinting in particular build up the calf muscles, these strains should be avoided.
What should I bear in mind during follow-up treatment after muscle surgery?
- Postoperatively, the legs are wrapped or a well-compressing support stocking is worn for approx. 3 months.
- Thrombosis prophylaxis with heparin depending on the degree of immobilization.
- Hospitalization is recommended for at least 24 hours.
- Crutches provide safety for the first 2 – 3 days.
- Particularly in the first 2 weeks after calf reduction, physical restraint and elevation of the legs is recommended.
- You should abstain from sport for approx. 6 weeks.
- Full functionality of the calves after a few weeks.
- It can take more than 6 months for the calf muscles to regain full strength.
Fact check after surgery
- Practitioners: Dr. Schumann and Dr. Schumann-Averkiou
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia
- Hospital stay: 1 day inpatient
- Follow-up treatment: Thrombosis injections, support stocking, crutches
- Sport: Abstain from sport for 6 weeks
Related topics and further information
Technical terms:
- Gastrocnemius muscle = calf muscle, an auxiliary muscle
Related topics:
Further information: