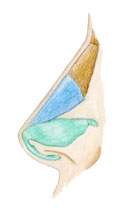
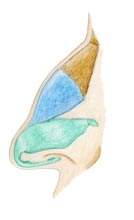
The anatomy of the nose is crucial for rhinoplasty. The image on the right shows, for example, the humped nose or humped long nose:
- green: wing cartilage
- blue: triangular cartilage
- brown: bony nasal roof
The nasal roof with bony and cartilaginous parts of the bridge of the nose is shaped during the operation. The fixed area consists of the nasal bone and the bony part of the nasal septum on the inside. The area further down is more or less laterally movable and consists of cartilage. The roof is bordered here by the so-called triangular cartilage (blue). The cartilaginous part of the nasal septum is located deeper down.
The tip of the nose is characterized by the shape of the wing cartilages (green), which stretch out like two half umbrellas. These two structures are usually easy to feel and are visible in many people.
Correction of the cartilaginous nasal septum
When correcting the nasal roof, the triangular cartilage (cartilaginous part of the nasal roof) is also adjusted as part of the rhinoplasty procedure. At Yuveo Düsseldorf, we then also have to modify the anterior nasal septum. This results in a lowering of the tip of the nose and the lower part of the nasal roof.
For plastic surgery on long noses or hooked noses, our Düsseldorf plastic surgeons shorten the lower end of the nasal septum so that the tip of the nose can be positioned upwards.
Misalignment of the nasal septum with nasal breathing obstruction
The straightening of the septum should also be included here. This is possible by means of relieving incisions, fixation of cartilage grafts and specially applied sutures.
Only in rare cases, when the nasal anatomy shows a complex curvature of the nasal septum, can we remove it completely, straighten it outside the body and then reinsert it.
The nasal anatomy determines the angle between the nasal bridge and the upper lip line.
During rhinoplasty, we must pay particular attention to the angle between the bridge of the nose and the upper lip. This angle, which is easy to assess in profile, plays a major role in the aesthetics of the nose and therefore in rhinoplasty.
While an obtuse angle of 100 to 110 degrees is considered aesthetic for women, this is between 90 and 100 degrees for men.