Tendovaginitis stenosans means constricting tendon sheath inflammation. The classic form is the so-called fast finger or snapping finger. In tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain, the constriction is localized at the 1st extensor tendon compartment.
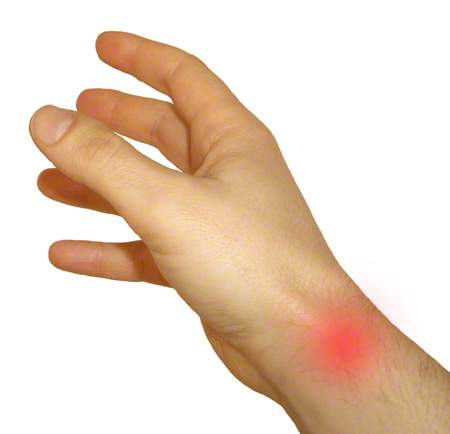
Figure: Typical pain region (red) in tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain in the area of the 1st extensor tendon compartment.
Development of tendovaginitis de Quervain
Tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain, also known as housewife’s thumb, can be caused by overloading, tendon sheath irritation, tendon sheath inflammation and a certain individual tendency. The German term Hausfrauendaumen (housewife’s thumb) illustrates the fact that women are significantly more frequently affected than men.
Swelling of the tendon sheaths on the thumb side of the wrist causes relative constriction in the first extensor tendon compartment. This leads to pain in this area and further irritation of the tendon sheath, which in turn increases the symptoms.
Anatomy
Tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain is anatomically localized in the area of the first extensor tendon compartment on the part of the radius close to the wrist. Two extensor tendons of the thumb run through the first extensor tendon compartment on the thumb side of the wrist. This has the function of a guide rail for these tendons. This extensor tendon compartment is often divided into two sections, which must be taken into account during surgery.
The following complaints can occur with the housewife’s thumb.
Tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain is typically characterized by pain in the wrist on the thumb side, which can extend into the forearm and up to the elbow. Despite the term “housewife’s thumb”, the condition also occurs in men, although it is more common in women. The symptoms usually occur during exertion and when the thumb is spread apart. There may also be rubbing in the area of the extensor tendon compartment or, in rare cases, even a snapping phenomenon similar to that of the jumping finger. The wrist shows swelling on the thumb side and is very sensitive to pressure. Wrist pain should be differentiated from the symptoms of tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain.
If the examiner flexes the wrist together with the thumb in the direction of the little finger, the affected person often feels a shooting pain that originates in the area of the first extensor tendon compartment. This is referred to as a positive Finkelstein sign.
Treatment of Tendovaginitis de Quervain without surgery.
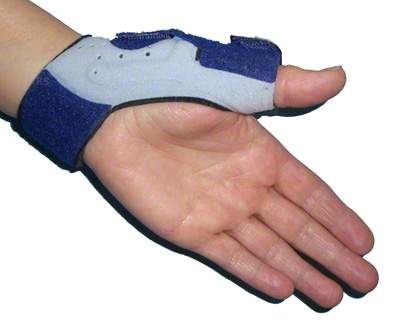
Image: Removable thumb splint for immobilization with Velcro fastener.
In the early stages of tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain, cortisone injections applied to the extensor tendon compartment can reduce the swelling of the tendon sheath and reduce the inflammatory processes. The tendon can now glide freely again and the vicious circle of irritation – movement – irritation is broken. Unfortunately, the therapeutic success is not always long-lasting. This can result in new injections or an operation. When giving the injection, the tendon should not be punctured directly. This is because the cortisone has a weakening effect on the tendons, which can result in a tendon rupture.
Conservative treatment:
- Decongestant measures: Cooling, voltaren ointment, arnica balls or tablets if necessary
- Painkillers: As an accompanying measure, NSAIDs(non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can be prescribed temporarily for tendovaginitis de Quervain in order to reduce pain and swelling.
- Cast immobilization: Immobilization for a few weeks is advisable to reduce the movement of the tendons in the tendon compartment and thus reduce the irritating effect that maintains the tendon sheath inflammation. More comfortable to wear than a standard cast is the thumb splint shown in the picture, which is also used for thumb saddle joint arthrosis. Simple wrist splints are not ideal for a housewife’s thumb, as the thumb can continue to move!
The operation for tendovaginitis de Quervain is called extensor tendon compartment splitting.
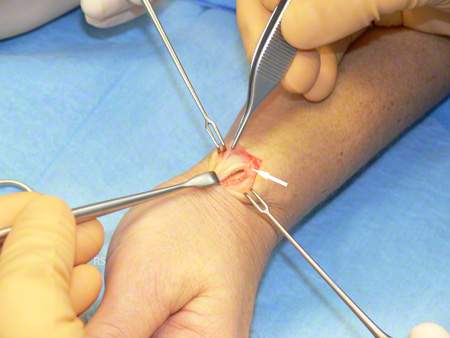
The aim of surgery for tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain is to achieve lasting therapeutic success. The procedure can be performed under local anesthesia or iv. Regional anesthesia (forearm anesthesia). After making a skin incision over the first extensor tendon compartment in the area of the thumb-side wrist, the surgeon splits it and checks the tendon function. If necessary, part of the swollen tendon sheath is removed to eliminate the constriction. Care must be taken to ensure that the cutaneous branch of the radial nerve is not severed. Otherwise, the typical symptoms of tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain will have disappeared, but a feeling of numbness will remain on the back of the thumb. Furthermore, a split extensor tendon compartment should be identified so that both extensor tendons of the thumb can also be released.
Postoperative treatment of the housewife’s thumb.
Following the operation for tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain, a plaster splint is applied for about a week to immobilize the joint. The stitches are removed after 14 days. Independent movement exercises are started from the second week onwards. Physiotherapy and occupational therapy also accelerate the healing process.