Wrist pain is a common complaint not only in hand surgery. The possible causes / differential diagnoses are manifold. The most important causes of wrist pain are presented below:
Wrist pain with carpal tunnel syndrome
In addition to tingling and numbness, carpal tunnel syndrome also causes pain in the wrist, which can extend into the arm or even the shoulder. The pain is often worse when the wrist is strained or bent to its end position. A frequent occurrence of the symptoms at night is also typical of this disease.
The ganglion is a common cause of wrist pain
The ganglion / ganglion on the wrist can also cause pain. This pain is usually found where the ganglion is located. There are also so-called occult ganglions, i.e. ganglions that are not visible, which can cause wrist pain.
Rhizarthrosis – osteoarthritis of the thumb saddle joint
Rhizarthrosis, also known as thumb saddle joint arthrosis, usually manifests itself through load-dependent pain at the transition from the thumb (1st metacarpal bone) to the wrist.
Tenosynovitis of the wrist
Tendonitis of the wrist is also usually accompanied by pain. A large number of tendons run along the flexor and extensor side of the wrist, the tendon sheaths of which can become irritated for various reasons. This results in pain in or near the wrist, which is often combined with swelling and redness.
Tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain
Tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain, commonly known as housewife’s thumb, is a special form of tendovaginitis. The pain is localized in the wrist on the thumb side, radiates more frequently towards the forearm and is intensified under stress.
Pain with special bone diseases and malformations of the wrist
-
- Bone cysts on the wrist, such as enchondromas, which consist of cartilage accumulations in the bone, can also cause pain. This is particularly the case if the bone has collapsed or fractured due to a significant increase in size. For this reason, bone cysts should also be ruled out by X-ray if wrist pain occurs without a clear cause.
Lunate malacia – lunate necrosis – Kienböck’s disease:
Pain in the wrist during exertion and later also at rest are the typical symptoms of this hand disease. The cause of the slow death of the bone is unclear. Chronic damage, e.g. caused by jackhammers, is recognized as an occupational disease in certain cases.- Scaphoid necrosis – scaphoid malacia – M. Preisler:
Similar to lunate malacia, scaphoid necrosis is a hand disease of unknown cause in which bone dies off. Here too, wrist pain is the main symptom.
The ratio of the length of the ulna and radius near the wrist
An ulna that is too short(ulna minus variant) can cause pressure on the radius-side part of the wrist because the radius is relatively too long. This is associated with pain in this area. This can also promote the lunate malacia described above.
If the ulna is too long(ulna plus variant), pressure and subsequent pain can be found on the little finger side of the wrist.
The complaints can usually be treated well by surgically correcting the length of the ulna.
Injuries
Wrist pain is of course very common with injuries such as fractures, strains, bruises, ligament injuries and others. Treatment depends on the injury in question. The basic principles are Immobilization, cooling, elevation, pain therapy and decongestant measures, etc. Even with a minor strain and good treatment, the pain in the wrist can persist for months.
- Injuries sustained instead
Injuries can lead to renewed pain in the wrist even after many years. If a wrist fracture has healed in the wrong position or in the event of incorrect loading due to a torn ligament, this can lead to premature wear and tear (osteoarthritis) in the wrist with pain. - Discus triangularis
Wrist pain, particularly on the little finger side, can also be caused by an injury to the discus triangularis. This is a fine cartilage plate in the joint, similar to the meniscus in the knee, which can be torn or ruptured or cause pain in the wrist due to a contusion.
Overuse pain
Wrist pain is very common even without an acute injury due to chronic overloading of the wrist. The causes can be occupational or sporting in nature. In this case, recurring irritation (repetitive injury) of the joint or the surrounding tissue due to micro-injuries triggers the pain in the wrist. Avoiding the trigger is of the utmost importance in treatment. Treatment can also be carried out as described in the ‘Injuries’ chapter. In principle, overuse pain can occur in various structures of the wrist. Two particular forms are described below:
- Pisiformitis – irritation of the pea bone
The pea bone is a small, easily palpable bone to which the FCU tendon (flexor carpi ulnaris) attaches. Similar to tennis elbow, overuse symptoms can occur here, with chronic pain on the flexor side of the wrist on the little finger side. - FCR tendon irritation
As described for pisiform arthritis, there is also the possibility of irritation of the FCR tendon (flexor carpi ulnaris), which causes pain on the flexor side of the thumb wrist.
Pain in osteoarthritis of the wrist
Wrist arthrosis is a wear-and-tear disease that initially shows up on X-rays as calcium deposits, cartilage atrophy and later without a joint space with bone deposits and cysts. The severity of the pain in the wrist is highly variable. Osteoarthritis can affect the entire wrist = carpal, the part on the little finger side = ulnocarpal, the part on the thumb side = radiocarpal or individual carpal bones. Accordingly, the localization of the wrist pain already indicates which bones or joints are involved in the osteoarthritis.
Chronic polyarthritis and other forms of arthritis
Chronic polyarthritis is a systemic disease that usually begins with pain, swelling and restricted movement in small joints. If wrist pain is unclear, it should be ruled out by a rheumatologist.
So-called reactive arthritis occurs after intestinal or urinary tract infections (Reiter’s syndrome), whereby no germs but antigens are detectable in the joint. Such arthritis can also affect the wrist with pain, swelling and overheating.
In infectious, bacterial arthritis, germs can be detected in the affected joint. In addition to pain, swelling and overheating, fever is also present.
There are a number of other joint inflammations = arthritides and rheumatic diseases that can be accompanied by pain in the joints, including the wrist. However, several joints are usually affected.
Rare causes of wrist pain
Gout (hyperuricemia) and pseudogout (chondrocalcinosis) can also lead to wrist pain. In the case of gout, which is caused by uric acid deposits, it is usually not the wrist that is primarily affected by the pain, but rather the metacarpophalangeal joint, metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb, ankle joint and knee joint. In pseudogout, special calcium crystals are deposited and usually cause pain in the knee joint. The wrist is rarely affected.
Further information on hyperuricemia can be found in the Medinfo section on gout.

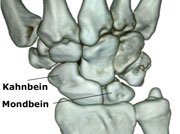 Lunate malacia – lunate necrosis – Kienböck’s disease:
Lunate malacia – lunate necrosis – Kienböck’s disease: