Sulcus ulnaris syndrome (S.-u.-S.), also called cubital tunnel syndrome by hand surgeons, is a nerve compression syndrome similar to carpal tunnel syndrome and Loge de Guyon syndrome, in which pressure damage is caused to nerves.
The ulnar sulcus is the ulnar canal through which the ulnar nerve passes.
Various factors can be involved in damage to the ulnar nerve. Often, however, no specific cause can be identified.
A chronic pressure load (e.g. arm support when driving), fractures, tumors(lipomas, ganglions, …), an X-misalignment of the elbow or signs of wear and tear can be decisive factors.
Some patients like to sleep with one arm behind their head, which stretches the nerve and presses it against the bony floor of the olecranon. This is often enough to cause pressure damage.
Even an impact against the nerve, which is associated with an electrifying pain, can lead to swelling, scarring and thus to the disease described here.
Contents
Yuveo Clinic
Special features of the treatment of the damaged ulnar nerve
Before the operation, the nerve conduction velocity of the ulnar nerve is measured.
Causes
Complaints
Conservative treatment
Sulcus ulnaris syndrome: surgery at Hand Surgery Düsseldorf
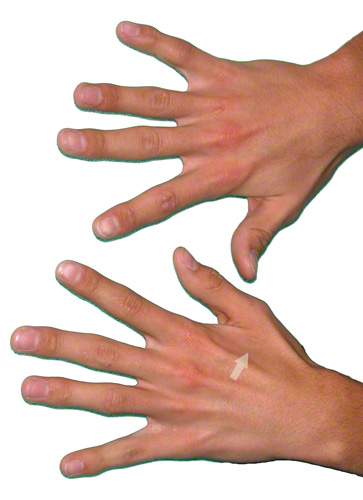
Advanced sulcus ulnaris syndrome, especially if significant muscle atrophy of the hand is visible (see illustration on the right), should be operated on, otherwise the nerve can no longer be expected to heal.
We make an incision (5-8 cm) on the ulnar side of the crook of the elbow. Our hand surgeons then expose the ulnar nerve in the ulnar canal.
The nerve is then freed from constricting structures (connective tissue, muscle fibers, etc.).
In selected cases, our Düsseldorf hand surgery team must consider relocating the nerve to the soft crook of the elbow in order to prevent renewed pressure damage.
We can perform the procedure at the Yuveo Clinic in Düsseldorf on an outpatient basis if there are no reasons (secondary diseases) for not doing so.
An iv. Regional anesthesia, plexus anesthesia(anesthesia in the armpit) or, in special cases, general anesthesia are possible anesthetic procedures.
Image: Operation for sulcus ulnaris syndrome. The ulnar nerve (held with a rubber band) is detached from adhesions and constrictions in the ulnar canal.
Frequently asked questions about sulcus ulnaris syndrome
What are the typical symptoms of sulcus ulnaris syndrome?
At the beginning, sulcus ulnaris syndrome is often characterized by discomfort in the little finger and ring finger (on the little finger side).
This is later joined by a loss of strength in the hand and a loss of sensation in the little finger and ring finger (on the little finger side).
Tapping the ulnar nerve in the ulnar canal often triggers an electrifying sensation that extends into the little finger.
In advanced stages, the small muscles of the hand become entrenched, resulting in hollow-like depressions in the space between the metacarpal bones.
This is particularly noticeable between the thumb and index finger.
As explained by our hand surgeons in the case of Loge de Guyon syndrome, an imbalance of the musculature develops as a result of the entrenchment, which can lead to a so-called claw hand.
How is conservative treatment carried out in hand surgery in Düsseldorf?
The measurement of the “nerve currents” (= ENG / EMG) by the neurologist should confirm the suspicion of a constriction in the olecranon.
Compression(crushing) of the ulnar nerve in the Loge de Guyon should also be ruled out in this context.
This measurement is essential before an operation and should be relatively up-to-date so that the hand surgery team has a reference for the check-ups after the operation.
Before operating on sulcus ulnaris syndrome, our hand surgeons recommend that a conservative treatment attempt be made first if the symptoms and the electrophysiological examination by the neurologist allow it.
There are various therapeutic approaches:
Vitamin B6 preparations and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often prescribed. A positioning splint at night can also help to alleviate the symptoms. Avoiding triggering stress (resting the elbow on an armrest, etc.) is also helpful in some cases.
Corticoid injections should only be given in acute pain situations, as this can lead to permanent nerve damage.
What advice do our hand surgeons give you after the operation?
In sulcus ulnaris syndrome, the regeneration of the nerve from the crook of the elbow to the hand is a long process. Patience is required for up to 6-9 months to achieve a significant improvement, especially in the sensation of feeling. In contrast, the shooting pain often improves very quickly.
If the pressure on the nerve has persisted over a long period of time or was particularly intense (injuries), the loss of sensation and the atrophy of the small hand muscles often do not fully recover. For this reason, our hand surgeons advise that you should not wait too long before undergoing surgery.
Once the sulcus ulnaris syndrome has been operated on at the Yuveo Clinic, the patient then wears an upper arm plaster splint for 14 days to immobilize it. Careful movement exercises in the elbow joint can then be started. Depending on the severity of the condition and the healing process, we also recommend physiotherapy.
We remove the stitches after approx. 14 days. We recommend a neurological-electrophysiological check-up with a neurologist after about 4-6 months. However, signs of improvement in the measured values can often only be found after 6-9 months.
Fact check for surgery
- Practitioners: Dr. Schumann and Dr. Schumann-Averkiou
- Anesthesia:
Anesthesia of the armpit, general anesthesia if necessary - Hospitalization:
outpatient - Follow-up treatment:
Upper arm plaster splint for 14 days, physiotherapy - Remove stitches:
after 14 days - Check-up: with a neurologist after 4 to 6 months
- Significant improvement in symptoms: after 6 to 9 months
Related topics and further information
Technical terms:
- Cubital tunnel syndrome synonymous with S.-u.-S.
- Ulnar nerve = ulnar nerve
- Sulcus = groove, channel
- Sulcus ulnaris = ulnar canal
- Ulnar groove syndrome synonymous with S.-u.-S.
Related topics:
Further information: