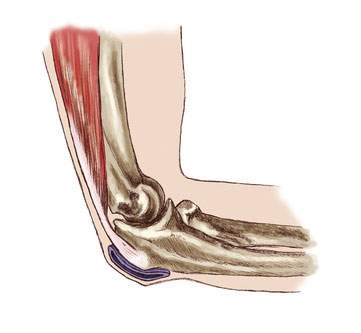
Image: Bursa on the elbow (blue).
Bursae (= bursa) are located in various places on the body as a displacement layer and to protect tendons, muscles and skin. Overloading can lead to irritation and ultimately to bursitis, which is known in medicine as bursitis.
The following forms of bursitis are possible:
- Acute bursitis
- Chronic bursitis
- Purulent bursitis = bursitis purulenta
- Inflammation of the bursa due to injury = bursitis traumatica, with bleeding also bursitis hemorrhagica
Causes and facts:
Bursitis occurs preferably in the elbow or knee. Other localizations affect the hip region (greater trochanter), the knee (in front of the kneecap), the shoulder, the Achilles tendon and the ball of the big toe, among others.
Bursitis can be caused by mechanical overload, as is often the case with tile layers on the knee. Injuries (e.g. bruising) can also lead to bursitis. The possible inflammatory causes are a joint infection or other infections. However, germs can also lead to infection via the bloodstream. This is the case, for example, with tuberculosis or gonorrhea = gonorrhea. Other causes include gout, inflammatory rheumatic diseases, autoimmune diseases and reduced immunity in various general diseases.
What symptoms are typical of bursitis?
Purulent bursitis usually begins quickly and is characterized by tenderness, swelling, redness and possibly overheating. If the lymph channels are affected, a red stripe appears. This is known as lymphangitis, in which lymph vessels are involved in the inflammatory process. If the germs (in 90% of cases staphylococci) reach the bloodstream (rather rare), fever is the result. A visit to the doctor should then no longer be postponed!
Chronic bursitis is usually characterized by swelling without the above-mentioned signs of inflammation. The bursa feels firm and elastic to the touch.
Pain is typically accompanied by a restriction of movement in the neighboring joint. In the case of bursitis of the hip, no redness is normally visible as the bursa lies deep under the muscles.
How is bursitis treated?
Other diseases should be ruled out before treating bursitis.
Conservative treatment:
Painful bursitis can be treated conservatively in the initial phase. Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) relieve pain and reduce swelling and irritation. Cooling, elevation and immobilization (plaster cast) are further important measures. If the bursitis is certainly not purulent, the irritating effusion can also be treated with a puncture or cortisone injection. A puncture can also make sense in the case of an irritable effusion or bruise caused by blunt force. However, it should be borne in mind that the treatment of bursitis by puncture or injection with cortisone can also lead to a secondary infection.
The bursitis usually disappears within a few weeks as a result of the measures mentioned here. Despite these conservative treatment options, a reliable cure can only be expected if the affected bursa is completely removed.
How is surgery performed for bursitis?
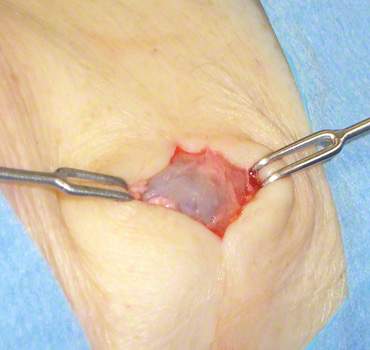
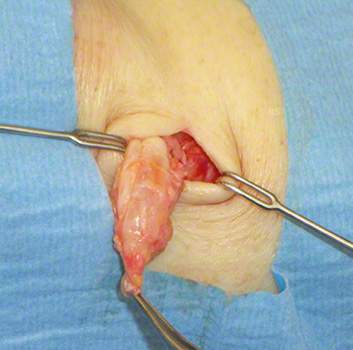
Figure: Surgery for chronic bursitis.
Chronic bursitis is operated on to prevent recurring relapses. It is also important to eliminate possible causes of bursitis. These can include bony protrusions or, for example, a malposition of the big toe (hallux valgus) on the foot.
Surgery for purulent bursitis requires antibiotic treatment (e.g. oxacillin) in addition to the removal of the bursa. If the inflammation is severe, initial treatment as for an abscess is appropriate. This means that the bursa is relieved through an incision and rinsed daily. Once the bursitis has healed, the bursa can be removed. This is called a two-stage procedure.
If a bursa has been opened during an injury (e.g. cut or laceration, etc.), it should be removed as part of the wound treatment in order to prevent protracted purulent bursitis.
What should I bear in mind after the operation?
The conservative treatment measures listed above are useful during and after the operation. A plaster splint is advisable for 7-10 days, depending on the localization.
How can bursitis be prevented?
Prevention is possible in the case of chronic bursitis.
- Treatment of the underlying disease: The underlying diseases described above should be treated as far as possible in order to reduce the risk of bursitis.
- Avoidance of triggering causes: Repetitive mechanical stress should be avoided. In the elbow, playing tennis and other similarly stressful sports can promote bursitis. Kneeling activities should be reduced on the knee.
- Compression: Bandages that provide compression in the area of the bursa can also be used to prevent bursitis in the elbow and knee.
- Padding: Avoid resting the elbow on hard surfaces for too long or kneeling for long periods without padding.
- Breaks: Take frequent breaks after strenuous and repetitive activities.