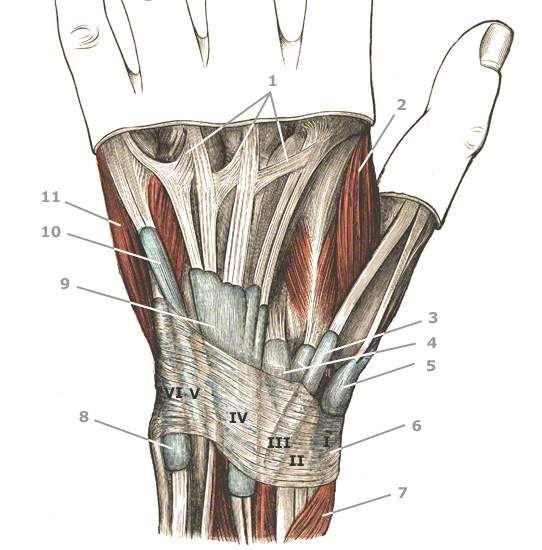
The tendon sheaths of the back of the hand run through the extensor tendon compartments of the hand.
In the main stress zone in the back of the hand, tendon sheaths have developed that form lubricating fluid (synovia) to facilitate the sliding of the extensor tendons. These tendon sheaths run along the back of the hand through so-called extensor tendon compartments. Similar to the annular ligaments on the flexor side of the fingers, the 6 tendon sheaths essentially serve to fix and guide the tendons in order to improve force transmission.
Extensor tendon compartments consist of coarse, firm fibers that attach to the bones of the carpus, ulna and radius. The continuous tendons belong to the extensors of the forearm muscles.
The following image illustrates the anatomy of the back of the hand and shows the relationship of the extensor tendons to the extensor tendon compartments of the hand:
- I-VI the 6 extensor tendon compartments
- 1, Connexus inertendinei are cross-connections between the extensor tendons on the back of the hand
- 2, M. adductor policis (thumb muscle); it can atrophy in ulnar sulcus syndrome and Loge de Guyon syndrome, resulting in the formation of a depression.
- 3, tendon sheath of the extensor pollicis longus = long extensor of the thumb
- 4, Tendon sheath of the extensor carpi radialis longus (right) and brevis muscles (left)
- 5, tendon sheath of the extensor pollicis brevis muscle (small thumb extensor) and abductor pollicis longus muscle (long abductor of the thumb)
- 6, Retinaculum extensorum = extensor carpal ligament
- 7, M. extensor pollicis brevis = small thumb extensor
- 8, tendon sheath (SSch) of the extenso carpi ulnaris muscle = ulnar extensor of the wrist
- 9, SSch of the extensor of the long fingers = M. extensor digitorum
- 10, SSch of the extensor digiti minimi = extensor of the little finger
- 11, M. abductor digiti minimi = abductor of the little finger
The first tendon compartment
Two tendons run through the first tendon compartment: The tendon of the extensor pollicis brevis muscle (small thumb extensor) and the abductor pollicis longus muscle (long extensor of the thumb).
Hand surgery this tendon compartment is of particular importance, as it is not uncommon for tendovaginitis to develop here. The inflammation here leads to a constriction of the tendon gliding tissue and the tendon in the 1st extensor tendon compartment and thus to tendovaginitis de Quervain, also known as housewife’s thumb, with corresponding symptoms.
If this condition requires surgery, plastic surgeons must bear in mind that the first tendon compartment is split in two in some cases. Both parts must therefore be severed, otherwise a relapse is inevitable.
In principle, this special form of tendonitis can occur in all extensor tendon sheaths, but it is most common in the 1st tendon sheath.