On this page you will find a representation of the superficial human anatomy. In well-trained athletes, especially strength athletes, the muscles lying on the surface are sometimes surprisingly easy to recognize. Even muscle fiber bundles are visible. The superficial parts of the skeleton are also examined. The links will provide you with further details on the musculature.
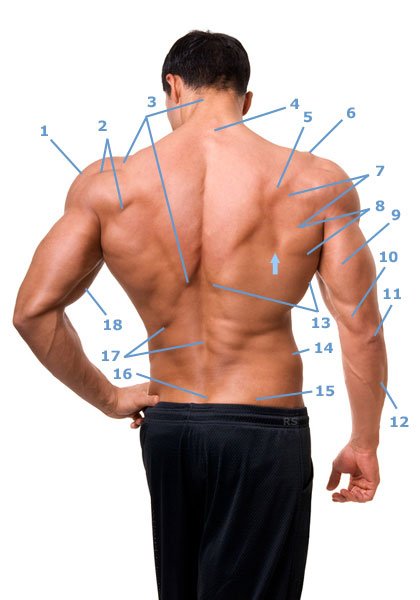
Back muscles, upper and lower arm
- 1, deltoid muscle: Pars acromialis
- 2, deltoid muscle: pars spinosum – shoulder blade bone part
- 3, The trapezius muscle with its trapezoidal appearance.
- 4, spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae
- 5, Bone of the scapula – Spina scapulae
- 6, Acromion of the shoulder blade
- 7, The infraspinatus muscle is located below the scapula (5).
- 8, The teres major muscle is visible between 13 and 7.
- 9, Long head (caput longum) of the triceps brachii muscle.
- 10, The medial head (caput mediale) of the triceps brachii muscle.
- 11, Elbow bone
- 12, The extensor carpi ulnaris muscle covers the ulna (ulna).
- 13, M. latissimus dorsi is the largest muscle in the human body in terms of surface area.
- 14, Dei Crista iliaca (iliac crest of the pelvic bone) is easy to palpate even in corpulent people.
- 15, M. glutaeus maximus – large gluteal muscle
- 16, sacrum
- 17, erector spinae muscle – extensor of the back. This musculature is made up of a complicated network of back muscles.
- 18, M. biceps brachii
- Arrow, The angulus inferior scapulae is the lowest tip of the scapula.
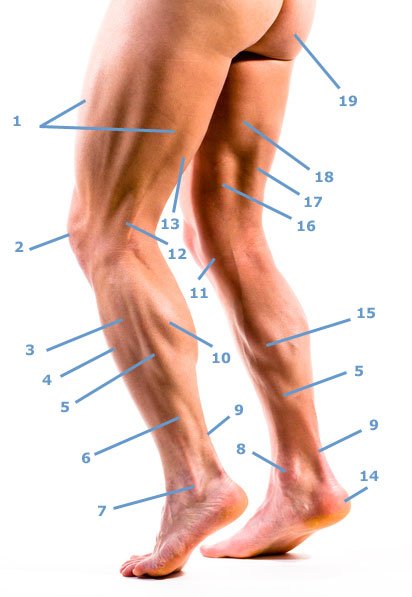
Leg muscles: thigh and lower leg
- 1, The vastus lateralis muscle is the lateral head of the quadriceps femoris muscle. The retractions in the middle of the vastus lateralis muscle are caused by the tension of the fascia lata.
- 2, Patella kneecap
- 3, Musculus peroneus longus upper part
- 4, The tibialis anterior muscle is conspicuous as a bulge lateral to the tibial crest.
- 5, The soleus muscle, the clod muscle, lies under the gastrocnemius muscle (10).
- 6, Musculus fibularis (peroneus) longus lower third
- 7, outer ankle
- 8, inner ankle
- 9, The gastrocnemius muscle (10) and soleus muscle (5) are anchored to the Achilles tendon.
- 10, The outer head of the gastrocnemius muscle is smaller than the inner head.
- 11, The pes anserinus goosefoot combines the tendons of the sartorius (sartorius), semimembranous (16), semitendinosus and gracilis muscles.
- 12, The tensed tendon of the biceps femoris muscle (17) (caput longum).
- 13, belly of the biceps femoris muscle
- 14, heel
- 15, gastrocnemius muscle (twin calf muscle) inner head
- 16, M. semimemranosus
- 17, M. biceps femoris
- 18, The adductors are only visible as a whole.
- 19, M. glutaeus maximus
- 20, vastus lateralis muscle in the picture below
- 21, vastus medialis muscle also shown in the picture below.
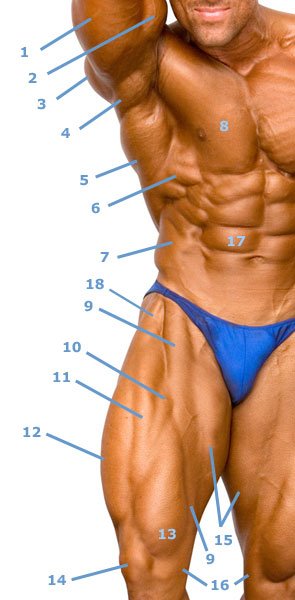
Chest, abdomen and thighs
The saw muscle (6) and the sartorius muscle (9) are particularly clearly visible in this image.
- 1, Musculus triceps brachii: The caput longum, the strongest of the three heads, is predominantly visible.
- 2, M. biceps brachii
- 3, pars spinosum (bone part) of the deltoid muscle.
- 4, M. teres major
- 5, The latissimus dorsi muscle is also called the cough muscle because of its function as an auxiliary respiratory muscle.
- 6, Of the serratus anterior muscle there are 3 strong prongs between the pectoralis (8), latissimus (5) and the external oblique abdominal muscle (7).
- 7, The fiber bundles of the obliquus externus abdominis muscle (external oblique abdominal muscle) can only be seen in this form in well-trained strength athletes.
- 8, pectoralis major muscle
- 9, The sartorius muscle is the longest muscle in the human body and attaches to the pes anserinus (16) together with other muscles.
- 10-13 and the vastus intermedius muscle, which is not superficially visible, form the quadriceps femoris muscle. This attaches to the tibial tuberosity via a fixation on the patella (14).
- 10 and 11, show parts of the rectus femoris muscle.
- 12, vastus lateralis muscle
- 13, vastus medialis muscle
- 14, patella, kneecap
- 15, The individual adductors cannot be distinguished.
- 16, Pes anserinus
- 17, M. rectus abdominis – One of the bellies of the right rectus abdominis muscle is marked. The abdomens are separated from each other by tendons called intersectiones tendineae. The vertical line between the straight abdominal muscles represents the linea alba of the abdominal wall (white line of the abdominal wall), which can be greatly dilated in rectus diastasis.
- 18, The tensor fasciae latae muscle inserts into the fascia lata.
Chest and arms (upper arms and forearms)
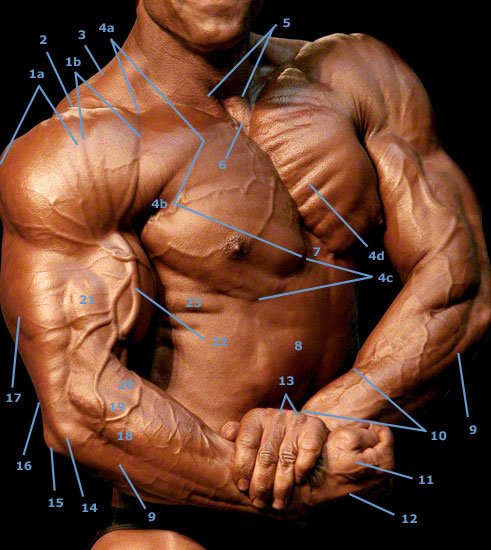
In this image, you should pay particular attention to the forearm muscles, which are very clearly visible. The muscle fiber bundles of the left pectoralis major muscle (4d) are also clearly visible.
- 1,a Pars acromialis of the deltoid muscle (deltoid muscle)
- 1,b The pars clavicularis of the deltoid muscle is called the clavicular part.
- 2, Acromion of the shoulder blade, which is connected to the clavicle via a joint. However, the clavicle is only partially visible due to the extreme muscle hypertrophy and the tension of the pectoral and deltoid muscles.
- 3, trapezius muscle – The pit between this hooded muscle and the clavicle is called the supraclavicular fossa major.
- 4, The pectoralis major muscle can be divided into the clavicular part (pars clavicularis 4a), the sternocostal part (pars sternocostalis 4b) and the abdominal part (pars abdominalis 4c). 4d marks one of several muscle fiber bundles of the large pectoral muscle.
- 5, The tendon parts of the inner head (caput mediale) of the sternocleidomastoid muscle on the right and left.
- 6, The jugular fossa (jugular fossa) is a cavity between 5, and the upper edge of the sternum.
- 7, Palpable bony processus xiphoideus at the lower edge of the sternum.
- 8, Straight abdominal muscle right
- 9, The extensor carpi ulnaris muscle is the extensor of the ulnar side of the wrist.
- 10, This bulge is formed by two muscles – the abductor pollicis brevis muscle and the extensor pollicis brevis muscle, the short thumb extensor.
- 11, interosseus dorsalis muscle of the hand with its two muscle bellies.
- 12, Tense finger extensor tendon
- 13, heads of metacarpal bones III and IV – On closer inspection, the finger extensor tendons can also be seen running over the heads.
- 14, Epicondylus radialis humeri
- 15, Olecranon in German elbow.
- 16, The tendon of the triceps attaches to the elbow (15).
- 17, The lateral head (pars lateralis) of the three heads of the triceps brachii muscle.
- 18, The extensor digitorum communis muscle is the common finger extensor.
- 19, The extensor carpi radialis longus muscle is the long radial extensor of the wrist.
- 20, The brachioradialis muscle is a powerful outward rotator of the elbow joint.
- 21, The brachialis muscle can be seen here between the biceps (22), triceps (17) and brachioradialis muscle (20).
- 22, The cephalic vein runs along the biceps brachii muscle and disappears into the depths between the deltoid muscle and the clavicular part of the pectoral muscle.
- 23, The serrations of the serratus anterior muscle (anterior saw muscle) attach to the ribs.